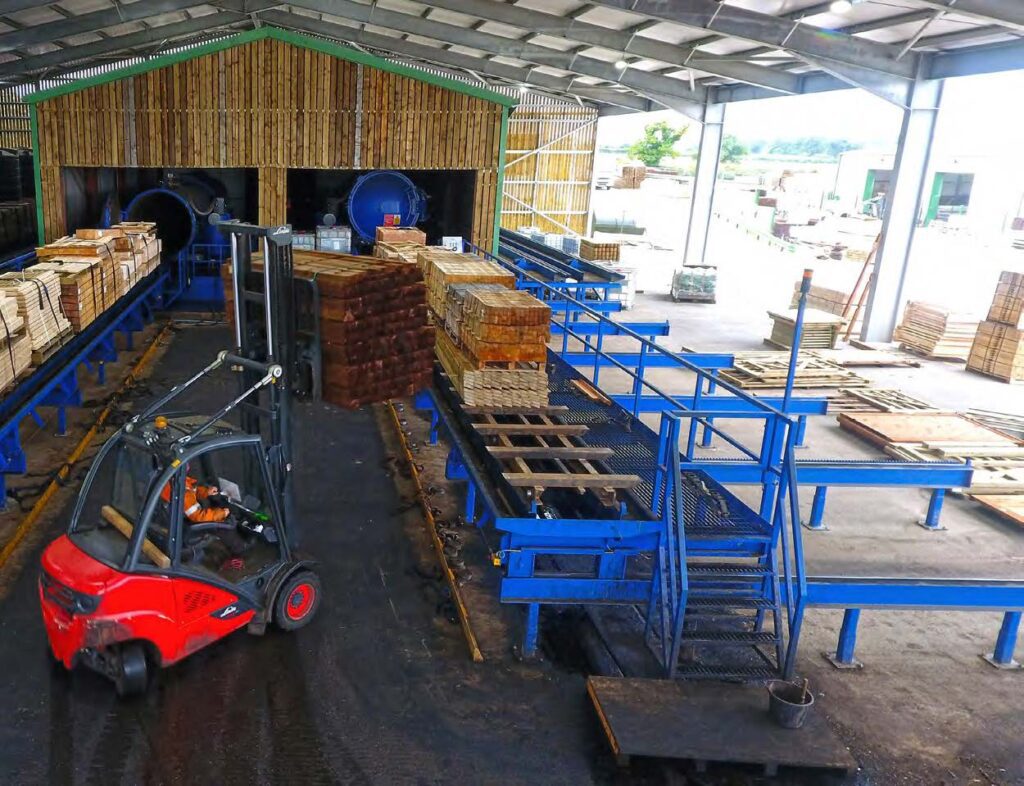
The companies within the woodworking industries are mostly SMEs with a few large groups operating on a national, regional or European scale. More than 365,000 businesses operate in the woodworking sector in Europe with about 8,000 (250,000 employees) of these businesses involved in wood treatment.
The wood treatment industry also known as wood preservation industry or wood preservation with chemicals can include different processes and different chemicals.
Each stage in the process of transforming wood into treated wood adds value that flows down the supply chain in the form of jobs, contribution to local economies and provision of durable materials for housing and infrastructure.
In Europe, it is claimed that there are approximately 250 installations with a production capacity of more than 75 m3 per day. However, accurate figures on the size distribution, production, employment or trade balance of the sector in the EU are lacking.1
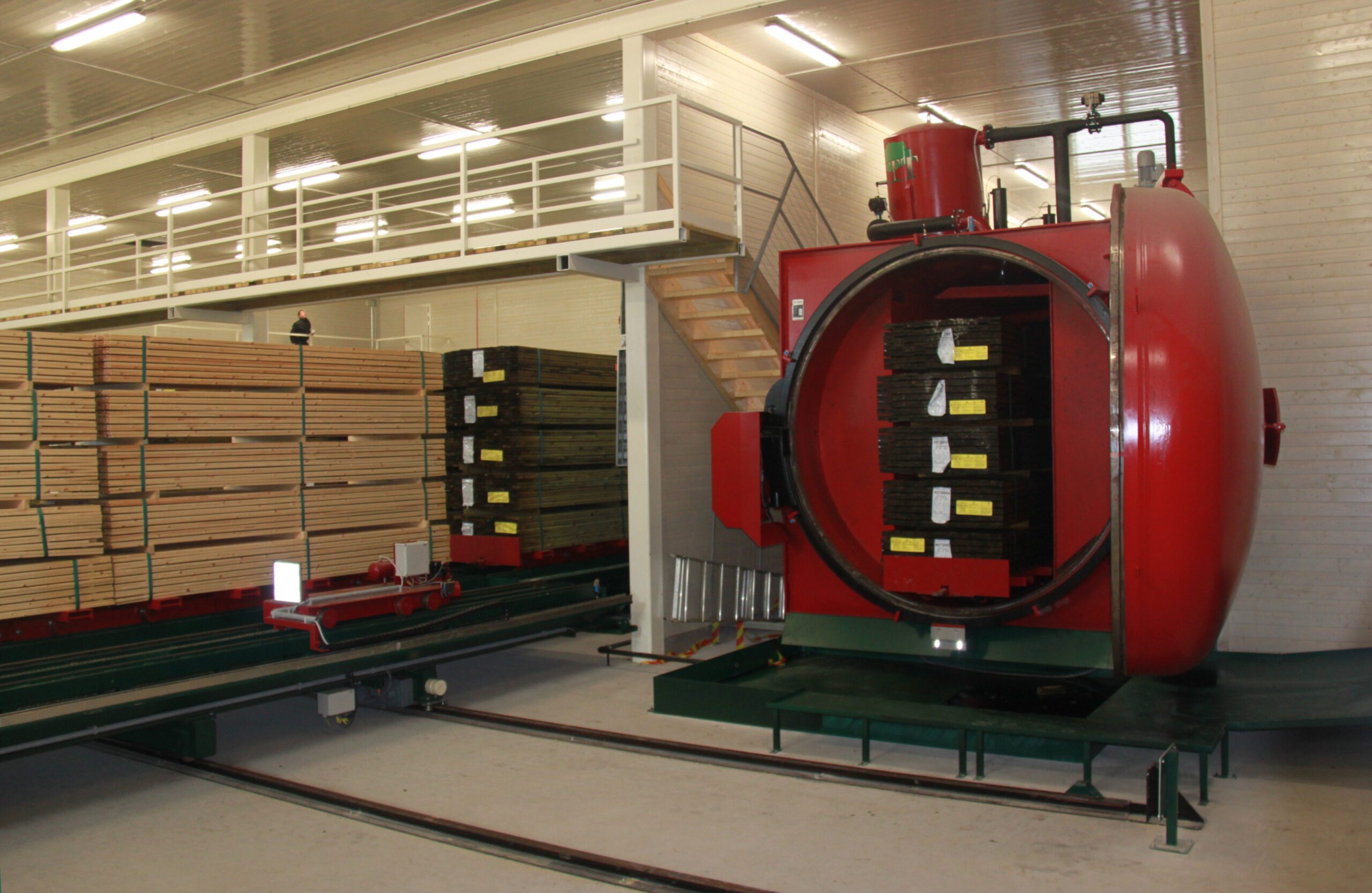


Wood may be treated in such a way that the amount of preservative and the depth of penetration into wood matches with the extent of the risk of attack by insects and fungi in service.
Treatment typically adds 2% to the cost of wood for Use Class 2, 3% for Use Class 3 and 5% for Use Class 4 for service lives up to 15 years. For increased service life (30 years and in some cases 60 years) treatment costs rise by only around 8%. These modest costs linked with exceptional extension to service life in challenging service situations compared with untreated wood confer economic benefit for house owners and society as a whole.2
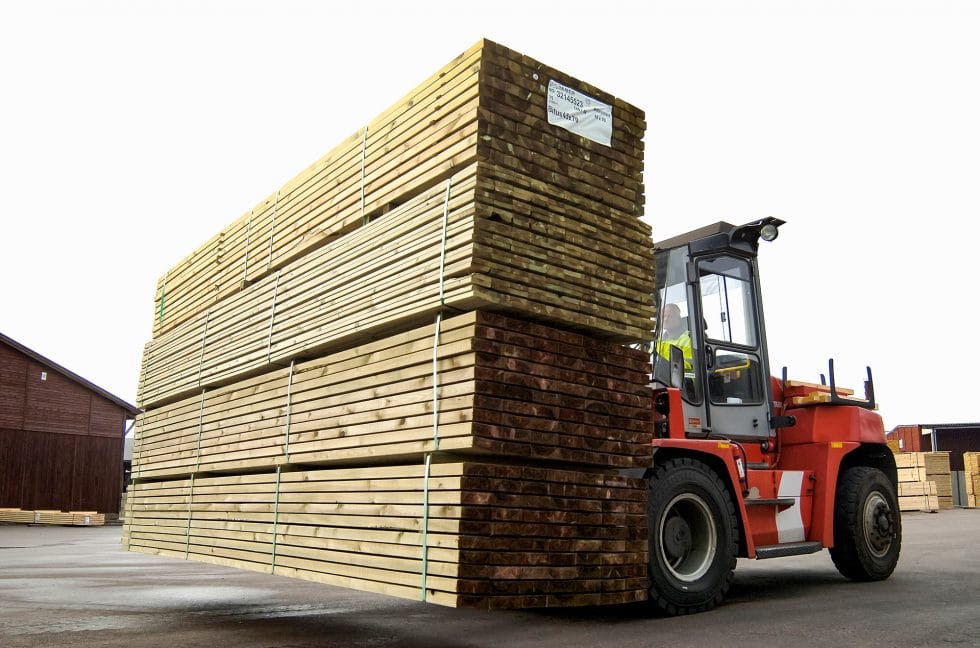


More than 365,000 businesses operate in the woodworking sector in Europe with about 8,000 (250,000 employees) of these businesses involved in wood treatment.