Technical development as well as public policies and regulations have helped to ensure that the use of treated wood in the EU is safe for consumers, workers, and the environment. For example, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and CLP (Classification, Labeling, and Packaging) regulations require manufacturers to assess the risks of chemicals used in treated wood and provide information on safe handling and disposal. The IED (Industrial Emissions Directive) sets limits on emissions from wood processing facilities to protect air and water quality.
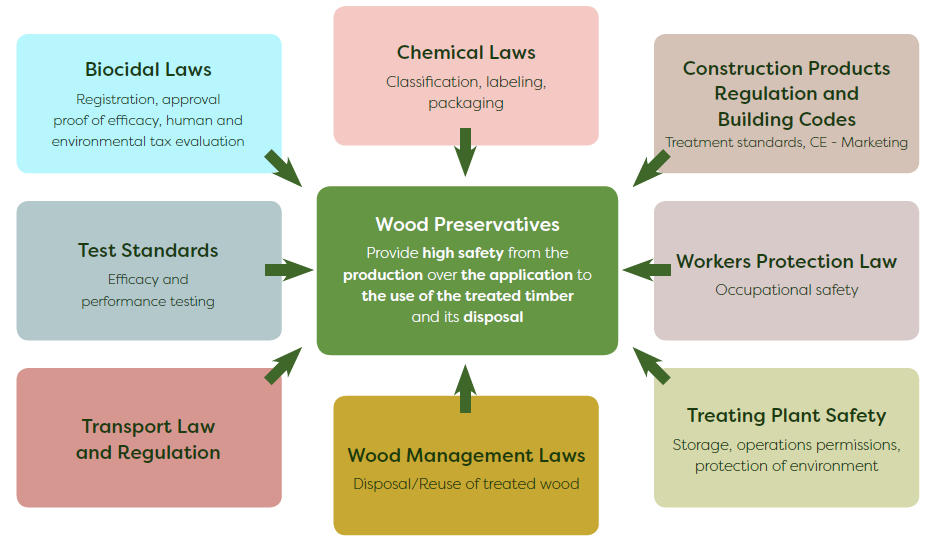
The BPR (Biocidal Products Regulation) ensures that the chemicals used in wood preservatives are safe and effective, and that they do not harm human health or the environment. Waste directives encourage the recycling and disposal of treated wood in a safe and environmentally responsible way.
Furthermore, there are several initiatives for sustainable use of building materials, such as the EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan and the Green Deal. These initiatives aim to promote a circular economy, reduce waste, and promote sustainable resource use, including the use of treated wood.
Overall, the combination of technical developments, regulations, and initiatives have helped to create a safe and level market for treated wood in the EU, which benefits both consumers and the environment.
Read more on this subject: Environment protection in EU
Read more on ECHAs webpage. https://echa.europa.eu/